

Non-Newtonian liquids deform at a different rate when the amount of shear stress changes - this rate can either increase or decrease with the increase in deformation, depending on the substance.Ī good example of a non-Newtonian fluid is ketchup. Fluids that deform at the same rate regardless of the force that causes this deformation are Newtonian. A distinction is usually made between two types: Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. Viscosity changes for different types of fluids.
To remove most of the oil from the car, they run the engine to warm it up, increasing the flow of the oil. Decreased viscosity of oil with an increase in temperature is a very useful property for auto mechanics who change the oil. When measuring viscosity for machine lubrication purposes, it is commonly measured for 40° C (104° F) and for 100° C (212° F).
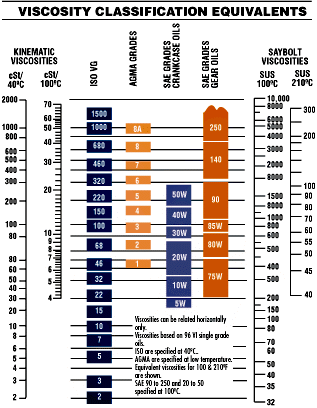
When measuring kinematic viscosity, it is important to specify which temperature it was measured for, because it differs with temperature for each substance. It is calculated as absolute viscosity divided by the density. Kinematic viscosity measures this resistance, as relative to the density of the substance. Absolute Viscosity and Kinematic ViscosityĪbsolute viscosity, also known as dynamic viscosity, measures the resistance of a fluid to a force that is acting upon it to make it flow. The latter is more often used in the automotive industry. There are two types of viscosity: absolute viscosity that is used more commonly in medicine, cosmetics, and cooking, and kinematic viscosity. Viscosity is a measure of internal resistance of fluid to the force causing the fluid to flow. Rotating bobs are more common, rotating cups reduce the likelihood of vortex formation, and "cone and plate" viscometers create a constant shear rate at any speed.This is what happens when a metal ball falls into a cup of non-viscous coffee Rotational viscometers use the concept of torque to measure the effort required to turn a disk or bob in a fluid.This can be done electronically for opaque fluids.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
